Like every other car, your Peterbilt 379 has different parts, each with its distinct benefits. From simple bolts and nuts to more sophisticated parts like the engine, your car is a complex combination of other elements.
The more you learn about some crucial parts, the better you can control and manage your car. The exhaust system is one such component, as it offers unique benefits to ensure the car’s maximum functionality.
To help you understand better, we’ll provide the diagram of the Peterbilt 379 exhaust system and discuss the function of each part.
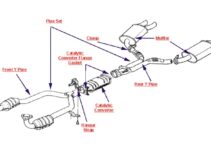
Peterbilt 379 Exhaust Diagram
Many people only know there’s an exhaust system underneath the car, and that’s it. It may surprise you that this component has different functions, including reducing engine noise, removing exhaust fumes, and increasing fuel efficiency. It does these functions with the help of the various elements incorporated in it.
Below is a diagram showing the different functions of the exhaust system:
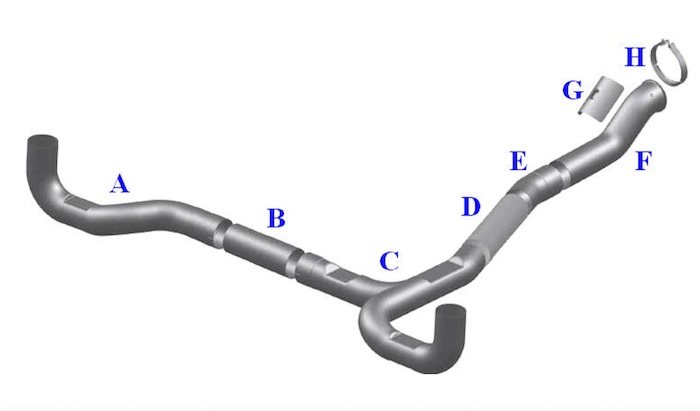
A. Exhaust left side
B. Exhaust Connector Pipe
C. Exhaust Pipe
D. Stainless Steel Flex Pipe
E. Exhaust Elbow
F. Exhaust Turbo Pipe
G. Heat Shield
H. Exhaust Turbo Clamp
Peterbilt 379 Exhaust System Parts Explained
The exhaust system is a series of interconnected pipes and devices that work harmoniously to increase car efficiency.
The exhaust pipe underneath the rear end of your car is a visible component of the exhaust system, but the system is far more complex and extensive. From just beneath the engine, the exhaust system travels along the undercarriage of your car, and it ends at the tailpipe.
The exhaust system on your car is designed to deal with the toxic emissions it emits. It will help keep the air clean by directing dangerous hydrocarbons away from the vehicle and passengers and lowering the air pollution your car emits into the surroundings. The exhaust system also significantly reduces car noise, an added benefit. Maintaining a functioning exhaust system will make your vehicle run smoothly and reduce harmful gasses.
What follows is an extensive explanation of the functions of each component in the exhaust system.
Exhaust Manifold
The engine block, front exhaust pipe, or catalytic converter are all connected by the exhaust manifold. The engine’s exhaust distributes wasted gas or exhaust fumes into the manifold at a very high temperature. It uses bolts to secure firmly to the engine and a gasket that sits between the manifold and engine block.
Catalytic Converter
Your car releases numerous fumes and gasses known as emissions while running. Emissions are responsible for air pollution. The exhaust system includes a catalytic converter, which aids in controlling emissions and making them more eco-friendly.
A catalytic converter converts dangerous gasses, such as carbon monoxide, from an engine’s exhaust into safe gasses, like water, using a chamber known as a catalyst.
Before being released into the atmosphere, it removes the potentially harmful molecules from vehicle emissions. Catalytic Converters are large metal boxes that are typically found underneath vehicles.
Exhaust Joints
Exhaust joints hold the slip-fit pipe connections and hangers in place. The four exhaust joints are the ball and socket, flat band, U-bolt, and V-band clamps.
Exhaust joints and hangers don’t need to be welded like most other exhaust system components. Consequently, replacing them is not too difficult. Your exhaust system’s components will disengage or become baggy without them.
Exhaust Pipe
The exhaust pipe in your car’s exhaust system runs from the exhaust manifold to the tailpipe, transporting engine exhaust fumes away from the vehicle. Typically, a tailpipe covers the exhaust pipe’s end.
This component extends from the rear of your car and lets the exhaust gasses out into the air. An exhaust leak from a damaged exhaust pipe could endanger nearby parts or start a fire
Exhaust Clamp
The overall exhaust system benefits from the use of exhaust clamps. They maintain the pipes’ integrity and make sure that none of the dangerous fumes can escape.
The sole function of the exhaust clamps is to secure separate pieces of pipe together without concern that they will separate. Some standard exhaust clamps include hanger clamps, U-clamps, narrow band clamps, lap band clamps, and V-band clamps. You must have these parts repaired right away if they break or become faulty.
Heat Shield
The placement of the exhaust system must keep the fuel supply, electrical wiring, or any other explosive parts of the vehicle from being burned, charred, or damaged.
A heat shield is a thermal barrier to keep things from overheating. They are frequently used to separate the engine block in the automotive industry to avoid heat danger to the bodywork and internal parts.
The primary purpose of the exhaust heat shield is to keep the interior of your car from becoming uncomfortable due to the extreme heat that comes from your exhaust. It shouldn’t be taken away.