Your car is your precious property that requires adequate maintenance. You should make a deliberate effort to ensure all the parts are properly maintained to make them work efficiently.
By becoming familiar with the different components of your Corvette, especially the exhaust system, you’ll be more in tune with it. You’ll also share your knowledge about specific symptoms with the mechanic so a proper diagnosis can be made in case of complications.
So, in this article, we’ll provide the diagram of the C4 Corvette exhaust system and explain the different components crucial to its functionality.
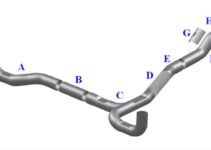
C4 Corvette Exhaust Diagram
The exhaust system of your C4 Corvette is one of the most crucial yet vulnerable components of the car, especially when overlanding or off-roading. Any problem with the exhaust can potentially alter the car’s performance.
Here’s the diagram of the C4 Corvette exhaust system:
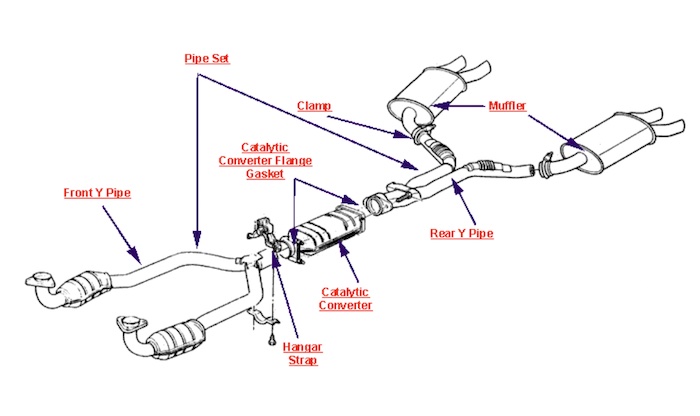
- Front Pipe
- Catalytic Converter
- Exhaust Clamp
- Pipe Seat
- Exhaust Hanger
- Muffler
- Rear Pipe
C4 Corvette Exhaust Diagram Parts Explained
Generally, a vehicle’s exhaust system comprises a complex system of pipes and devices with four crucial functions: remove toxic fumes from the engine, reduce engine noise, increase fuel efficiency and improve overall car functionality.
The exhaust system helps guide reaction exhaust times from the controlled combustion inside the engine. It conveys burnt gasses from the engine and safely dispatches them to the atmosphere.
Knowing the exhaust system will help you identify problems quickly. Below are the different functions of each component of the car.
Front Pipe
A crucial part of the converter assembly that significantly lowers gas emissions is the front pipe. Front pipes also called “downpipes,” join the exhaust manifold and catalytic converter.
Maintain this vital exhaust system part free of corrosion and leaks to ensure your car runs at its peak efficiency and gets better gas mileage. Front pipe leaks could produce noise and dangerous exhaust fumes. Replace it if it begins to exhibit wear and tear.
Catalytic Converter
Before being released into the atmosphere, a car’s emissions are separated by a catalytic converter to remove the potentially hazardous molecules. A catalytic converter requires a chamber known as a catalyst to change dangerous gasses like carbon monoxide from an engine’s exhaust into safe ones like steam.
This component is usually found under the car, and it looks like a large metal box. Two pipes are poking out of it. The catalyst and these two pipes help the converter prepare the gasses for release.
Exhaust Hanger
The mounts that are used to secure and support the exhaust pipes to the tail section of the car are known as exhaust supports or exhaust system hangers. Usually, rubber is used for the exhaust hangers so they can flex, absorb engine vibrations, and allow the exhaust to continue moving while the car is moving. The cabin’s noise level and pulse are improved by tightly fastening the exhaust.
When one or more exhaust system hangers are ineffective, the exhaust system may experience problems, which may also impact cabin comfort. A few symptoms that could indicate a potential issue with the car are typically the result of poor or unreliable exhaust hangers.
Exhaust Pipes
The exhaust pipes’ job is to link each component of the exhaust system. Steel, such as stainless steel or aluminized steel tubing, is typically used to make the pipes. These materials are highly long-lasting and corrosion-resistant.
The exhaust is efficiently directed toward the back of the car by the pipes. They are designed to keep the hot exhaust away from heat-sensitive components in the engine bay and along the vehicle’s undercarriage.
Tail Pipe
The tailpipe is the last part of an automobile’s exhaust system. The tailpipe, which protrudes from the muffler, is where the vehicle’s finished exhaust gasses are released. It is made of a metal that resists corrosion, like stainless or aluminized steel.
It’s the last part of the exhaust system, and it’s the most visible component from under the day. It safely directs the harmful fumes converted to less dangerous ones by the catalytic converter into the surroundings.
Muffler
Mufflers are made to reduce noise by using their noise-canceling ability. They are fixed parallel to the exhaust pipe. The muffler’s rubber and perforated chambers work together to dampen engine noise. The muffler’s chambers reverberate with the sounds that enter it. Due to this, the sound waves from the bounce start to produce and create opposing sound waves, which eventually eliminate one another.
To gain additional power, the mufflers also carry oxygen from fresh air. Your car runs more efficiently the faster it happens. For the vehicle to perform at its best, your car muffler must have an efficient exhaust flow. Some other car models use another part known as the resonator to support the muffler and ensure it effectively dampens the noise level.