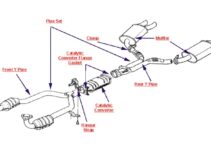
Your Mazda Miata, like every other gasoline-powered vehicle, has an exhaust system that helps minimize pollutants and transfer byproducts of gasoline combustion from the engine into the atmosphere. The exhaust system is the same for most vehicles.
The component has a significant impact on the way the car operates, sounds, and performs. As such, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental elements.
This article will reveal the Miata exhaust diagram and explains the different components that constitute it.
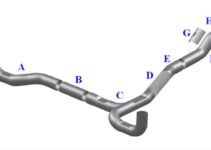
NA & NB Miata Exhaust Diagram
The exhaust diagram is a solid and robust component of the vehicle. It comprises several other components that work harmoniously to ensure you enjoy a smooth ride by reducing engine noises and pollutants.
Below is a diagram showing the different components that make up the Miata exhaust system:
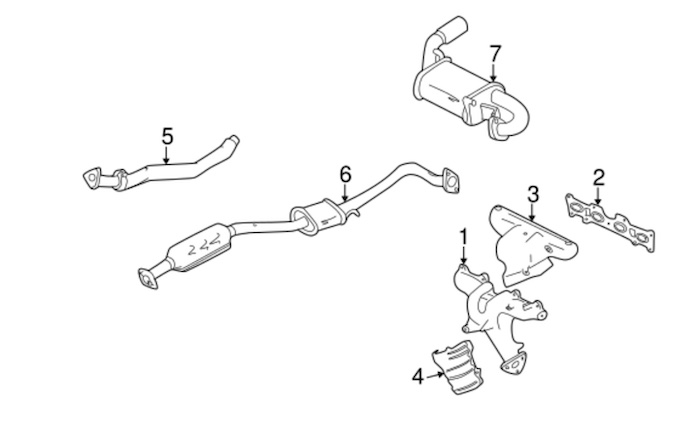
- Exhaust Manifold
- Manifold Gasket
- Heat Shield
- Heat Shield
- Exhaust Pipe
- Catalytic Converter
- Muffler
NA & NB Miata Exhaust Parts Explained
Ideally, your car exhaust system is an underrated component responsible for significant benefits to your car.
The exhaust system improves performance, reduces noise, moves gasses away from the front of the car, improves fuel efficiency, and more. It’s a complex system, and for the vehicle to operate at its best, many components must cooperate. Each piece has a specific contribution to ensure the system functions well. If there’s a problem with a part of the system, it will affect the car efficiently. But if everything works correctly, you’ll notice it while riding, as the ride will be quiet and enjoyable.
Let’s discuss the different functions of each part.
Exhaust Manifold
The first part of a car’s exhaust system is the exhaust manifold, which is explicitly fastened to the engine block. Exhaust manifolds accumulate engine exhaust gas from multiple cylinders and send it to the exhaust pipe. They are typically short-cast iron or stainless steel components. The exhaust gasses from several cylinders are combined into one pipe by an exhaust manifold.
The engine block is directly connected to the exhaust manifolds. Exhaust manifolds for flat engines or V-type will have two, one on either side of the cylinder bank. There is only one exhaust manifold on inline or straight engines, and it is situated between the catalytic converter and cylinder head.
Manifold Gasket
A gasket joins the cylinder head and manifold. As a result, the manifold can draw fresh air into the vacuum that the exhaust gas creates while also collecting waste gasses and sending them to the exhaust pipe.
The car will drive more smoothly and powerfully thanks to the exhaust manifold gasket. It is an instrumental part when the engine has to work hard. It’s crucial to remember that the exhaust manifold gasket plays a role in the catalytic converter’s protection and its other direct duties.
Heat Shield
The primary purpose of the exhaust heat shield is to stop the intense heat from your exhaust from starting a fire or even seeping into the cabin and irritating the passengers.
When your car is working or parked under grass or trees, during hot weather, the exhaust system can attain an extremely high heat that can directly impact the passenger’s comfort or even start fires in the cabin.
Additionally, the exhausts are heating up to the point where they could potentially burn several of the nearby parts. The exhaust heat shields are essential for keeping your cabin cool and avoiding fire hazards outside.
Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter, as its name suggests, aids in the transformation of harmful chemicals produced by the car engine into less toxic gasses released into the atmosphere. These chemicals are detrimental to humans and the environment if they are not converted.
The catalytic converter’s job is to assist in converting these toxins into harmless gasses. Carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons are some of the dangerous substances.
The performance and general health of the vehicle are directly affected by an effective catalytic converter. A car could run without it, but that is not sustainable. The oxygen sensors won’t function correctly without them. Additionally, the engine fault codes will appear and impact engine performance.
Muffler
A muffler or silencer is a device used to lessen the noise produced by an internal combustion engine’s exhaust, particularly one integrated into an automobile’s exhaust system.
Your car will sound loud if the muffler isn’t functioning correctly. Loud noises can indicate that your muffler needs to be replaced. Some vehicles also have standalone exhaust resonators to help dampen the exhaust noises. The resonators are included to assist the muffler in dampening the engine noise. They are usually in front of the muffler in the exhaust system.
Remember that an exhaust resonator isn’t made to lessen the exhaust’s volume. Instead, it eliminates and cancels out any “annoying” frequencies while leaving the “good” ones in place so drivers can enjoy them loudly.